The Role of Magnesium in Muscle Relaxation and Yoga Performance
Do your muscles feel sore more often lately after your yoga classes? It could be more than overexertion trying difficult yoga poses. The reason might be muscle stiffness that inhibits your flexibility,Magnesium Glycinate and it could be because of magnesium.
Magnesium in muscle relaxation is important because it helps your muscles contract, relax, and maintain electrolyte balance. That implies fewer cramps, deeper stretches, and more control with every yoga pose you hold.
Yoga emphasises controlled movement and consistent contraction and relaxation of muscles with every breath. Magnesium supports all that. Without enough magnesium, your muscles may not relax fully or recover properly.
In this article, we'll clarify the role of magnesium in muscle relaxation and why it matters for your yoga performance.
Photo by kike vega on Unsplash
Why is Magnesium in Muscle Relaxation Essential?
As magnesium is responsible for over 800 biochemical reactions in the body, it's important for muscle health. Yoga practice engages multiple muscles. It builds strength and endurance when you hold yoga poses for longer periods. Poses like plank, warrior I, bridge, etc, are known to strengthen core, back, and leg muscles. By lengthening muscles, yoga helps improve flexibility and range of motion.
So, after extended yoga sessions, you would experience muscle soreness. When you have adequate magnesium, your muscles can extend and flex better. This can help with post-yoga soreness. Magnesium also activates vitamin D and low levels of vitamin D can cause muscle weakness.
When there are high levels of calcium in muscles, it causes them to contract. Magnesium offers a counterbalance and balance calcium levels, allowing muscle relaxation after contraction. Knowing the importance of magnesium in muscle relaxation, you can ensure adequate magnesium intake.
Due to anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties, magnesium helps reduce overall muscular inflammation and oxidative stress. This supports effective muscle repair after yoga sessions. When you have stronger muscles, you can get more benefits from yoga and continue to practise power yoga, which ultimately can lead to overall health and fitness.
Boost Your Yoga Game With the Power of Magnesium
Yoga + magnesium can be a powerful combo. You do yoga daily to boost physical and mental health. It would be very interesting to note that magnesium mineral can support you in this goal. Magnesium not only supports physical health, but it also improves sleep, reduces stress and makes you feel more relaxed and confident.
Yoga practitioners can take magnesium to boost:
Emotional stability
Focus & concentration
Sleep
Self-awareness
Stress reduction
Digestion
Detoxification
Breathing
Immune function
How to Get Adequate Amounts of Magnesium?
Magnesium is not synthesized by the body and it's necessary to ensure that your diet contains adequate amounts of magnesium. The most common dietary sources of magnesium are:
Seeds
Legumes
Green vegetables
Nuts
Whole grain breads and cereals
Some fruits like raisins, dried apricots, and avocado
Seafood
On average, adult men need 400-420 mg of magnesium per day and women need 310-320 mg per day. However, dietary intake of magnesium often falls short and subclinical magnesium deficiency is more common. About two-thirds of Americans don't consume enough magnesium.
Poor dietary intake, impaired absorption, and age-related decline can all result in low magnesium in the body. To combat this, you can consider taking magnesium supplements that provide adequate amounts of magnesium. This can have a positive impact on muscle health and boost muscle-related physical performance.
Signs You May Have Low Magnesium
In healthy individuals, magnesium concentrations must be in the range of 0.75 to 0.95 mmol/L. If it falls below 0.75 mmol/L, it's called magnesium deficiency.
Initially, magnesium deficiency shows up as nonspecific symptoms. Some of the signs that your body shows indicating low magnesium are:
Muscle weakness
Muscular spasms
Reduced appetite
Fatigue
Nausea and vomiting
Prolonged magnesium deficiency can also cause
Muscle cramps
Numbness and tingling
Personality alterations
Depression symptoms
When there is critical magnesium deficiency, where the serum levels are lower than 0.4 mmol/L, it can lead to coronary spasms, abnormal heart rhythms, seizures, and ventricular arrhythmias. Every organ in the body will be impacted by magnesium deficiency.
What You Should Know About the Role of Magnesium in Muscle Relaxation and Recovery?
When you have a magnesium deficiency, the intracellular magnesium concentrations in your muscles may become depleted. It can show up as muscular tightness, stiffness, and cramps.
For yoga practitioners—whether you’re practicing gentle restorative yoga or the intense Bikram yoga method—muscle flexibility and relaxation are essential for holding poses safely and effectively. Without sufficient magnesium, your muscles may not perform at their best, which can affect your overall yoga experience and progress.
The integrity of skeletal muscles is also closely related to improved cognitive performance, attention, memory, and other executive functions. By keeping your muscles physically active through yoga practice, you can trigger the release of mood-boosting endorphins.
Due to aging, there may be reduced muscle function, which can restrict movements and it can impact emotional and mental wellbeing as well.
Often, active individuals have to manage delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS), which can cause stiffness and soreness in muscles after strenuous exercise. Appropriate magnesium levels in the body can help with optimal recovery and relieve muscle soreness.
Can Magnesium Boost Yoga Performance?
Magnesium is strongly associated with exercise performance. In a study, people who were given magnesium supplementation experienced improved exercise performance with Taekwondo training.
Taking magnesium before exercising or doing yoga may delay muscle fatigue due to its ability to decrease lactate accumulation in the blood.
It may also increase glucose availability. As your body relies on glucose levels for energy, it can result in improved performance.
Magnesium may reduce oxygen requirements in muscle cells during exercise and this can help with optimal physical movements with exercises such as yoga.
Broad Benefits of Magnesium
Beyond benefits for muscle contraction and relaxation, magnesium also has broad health benefits, including:
May reduce stress and symptoms of depression
Support for decreased anxiety
May help with migraine headaches
May improve symptoms like water retention, irritability, tiredness, and cramps related to Premenstrual syndrome (PMS) symptoms
May support better sleep, which is important for general health and performance
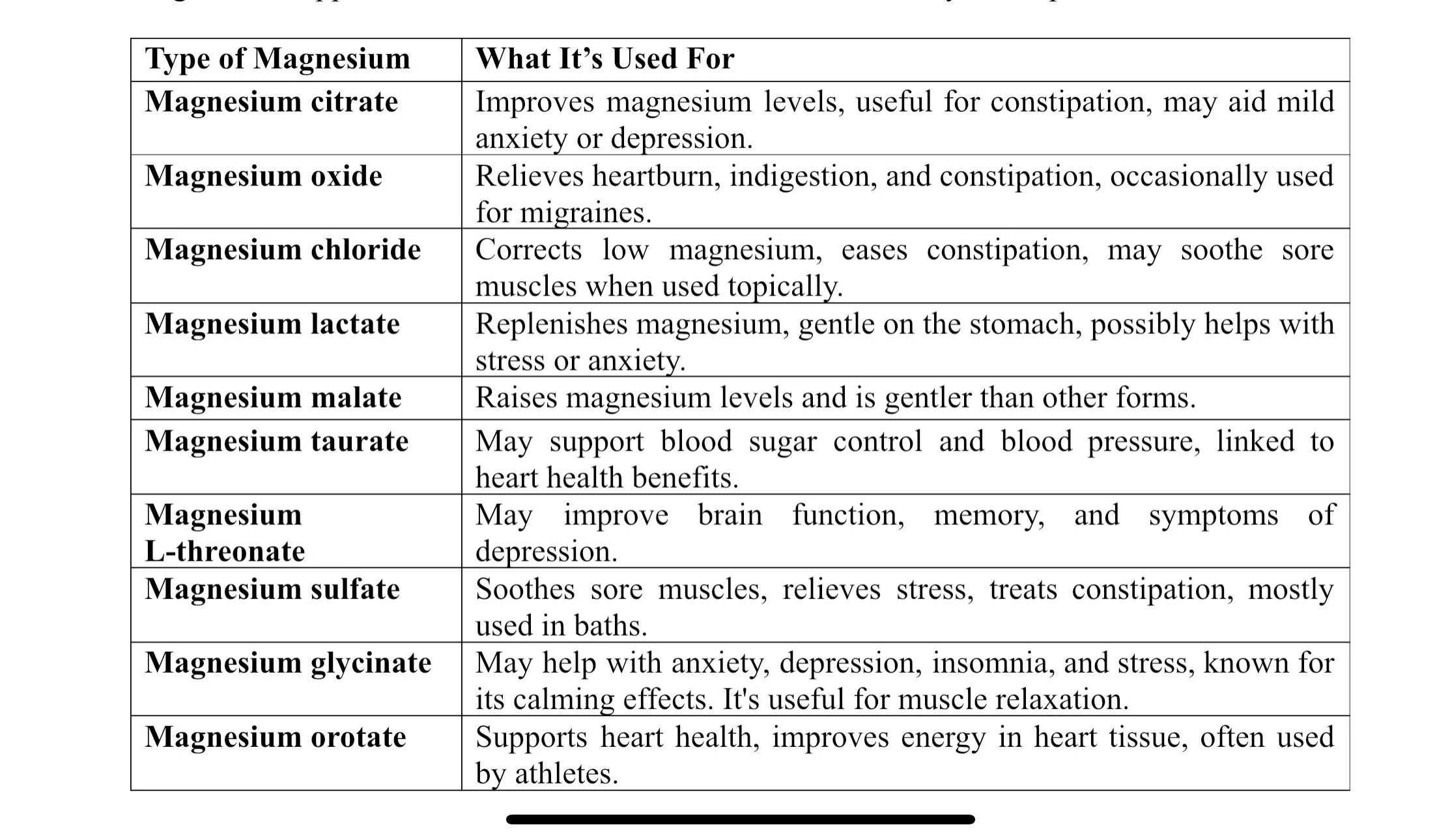
Different Types of Magnesium and Their Uses
Magnesium supplements are available in different forms and they have specific uses:
Best Types of Magnesium for Muscles
Among the different types of magnesium, some of the best types of magnesium for muscles are:
Magnesium glycinate – This is one of the most bioavailable forms of magnesium. It's gentle on the stomach and supports muscle repair and recovery. If you are looking for improvements in muscle relaxation, this can be a good choice.
Magnesium Chloride – It's the easiest form of magnesium, which can relax even rock oysters. It can be useful to soothe sore muscles, but it's widely used for topical applications. Bath salts often contain magnesium chloride as it's better absorbed via the skin.
Magnesium Sulfate – It's more commonly called as Epsom salt and it's used in relaxing bath soaks. It can be useful to relieve muscle soreness.
Different Forms of Magnesium
When you opt for magnesium supplements, you can choose different forms such as
Capsules
Liquid
Powder
Chewables
The type of magnesium and its concentration vary from one brand to another and also from one form to another. For example, Pure Encapsulations is a practitioner-recommended brand that has Magnesium Glycinate in both capsule and liquid forms. You should choose magnesium supplements based on your needs and also based on which form is easiest for you to take. Topical oils containing magnesium can be useful for achy muscles.
Who Can Benefit Most From Taking Magnesium for Muscle Relaxation?
Taking a blood test can reveal whether you have low magnesium. For healthy individuals without magnesium deficiency, diet alone may be sufficient. Even for those with deficiencies, including magnesium-rich foods in the everyday diet can be sufficient.
For individuals seeking to enhance muscle relaxation and optimize yoga performance, the best magnesium supplements can be a valuable addition, particularly if your diet is insufficient or if you experience absorption challenges.
Yoga can be useful to improve muscle strength in older adults and women. Athletes too practice yoga for active recovery. People with chronic diseases are also encouraged to do gentle yoga exercises for better health. Magnesium can help prevent muscle soreness, cramps, and fatigue as you engage them more during yoga sessions.
What are the Side Effects of Magnesium?
Excess magnesium from dietary sources doesn't pose health risks in healthy individuals. Hypermagnesia occurs when you take excessive amounts of oral magnesium, more than 2500 mg per day. It can result in stomach issues like diarrhoea, nausea, vomiting, and cramping. Sometimes, it may also cause headaches, drowsiness, or lightheadedness.
Excess magnesium may also cause muscle weakness, diminished or loss of deep tendon reflexes, or paralysis.
How to Safely Take Magnesium Supplements?
A blood test can reveal magnesium serum levels. When there is not enough magnesium in the blood, it may also indicate that your muscles don't get enough magnesium. You can consult with a health expert, and they may recommend magnesium supplements. In that case,
Choose high-quality magnesium supplements from trusted brands.
Follow the right dosage instructions and don't take more than recommended.
Look for the type of magnesium best suited for your body. Your healthcare provider can help with that.
Choose forms that are easy for you to take consistently.
Additional Tips for Effective Muscle Recovery
When you engage your muscles actively during yoga sessions, it's important to support their recovery too. Here are some useful tips:
Drink plenty of water before, during, and after yoga poses. Follow your yoga practitioner's advice for proper hydration.
Eat a healthy diet containing carbohydrates, protein, and healthy fats. Make sure to include fruits and vegetables that provide micronutrients.
Include rest days to boost recovery.
Get adequate sleep
If you wish to take supplements, always consult with a healthcare expert first.
Takeaway
Peak yoga performance is not only about regular practice. Smart nutrition also plays a key role in muscular performance and endurance. Whether you are flowing through vinyasas or holding poses for longer durations, your muscles must be able to contract and relax to improve fluidity in your yoga movements. Adequate magnesium levels in your body support your muscles and aid in recovery and repair. Ensure that you include magnesium-rich foods in your diet and if your healthcare provider suggests supplements, choose the right type and form that is best suited for your health goals and consistent consumption.
FAQs
Which magnesium is best for stress?
Supplements with magnesium glycinate for stress and anxiety are popular. They are highly bioavailable and are well-absorbed by the body. They can help reduce stress levels. Consult with an expert before taking supplements for stress.
2. When is the best time to take magnesium?
The best time to take magnesium depends on your health goals. If you are looking for sleep support, taking magnesium supplements before bed can be useful. For muscle recovery and repair, you may take it in the afternoon before your exercise session. Magnesium taken in the morning can help you manage stress and anxiety.
3. What is the difference between magnesium citrate and glycinate?
Both magnesium citrate and glycinate are different forms of magnesium that have distinct uses. Magnesium citrate is useful for digestive health to relieve constipation. Magnesium glycinate is known for its calming effects and is more suitable for anxiety and improved muscular function.
4. How long does it take for magnesium supplements to work?
The time it takes for magnesium supplements to work depends on your health. If you have a magnesium deficiency, improvements in blood levels may take a few months. On the other hand, fast-absorbing formulas like magnesium glycinate can be useful to relieve muscle cramps within 1 or 2 days. You may notice improvements in sleep in a few weeks and you may experience more calmness after taking magnesium for a few months.
5. Is magnesium in muscle relaxation important?
Yes, magnesium plays a crucial role in muscular function, contraction, and relaxation. It helps maintain electrolyte equilibrium, energy production, and protein formation – all of which are important for muscle health.
6. What are the physical benefits of taking magnesium when I practice yoga?
Yoga offers numerous health benefits for your body and mind. Ensuring adequate levels of magnesium when you practice yoga can help with
Reduced Risk of Being Injured
Better Muscle Performance
Improved Body Awareness
Decrease in Muscle Soreness
Enhancement in Overall Strength
Quicker Recovery
7. How can yoga and magnesium support me mentally and emotionally?
Yoga is not just about physical transformation. It offers emotional stability because the whole concept of yoga is bringing the mind and body together to focus on achieving inner stability and peace. Magnesium also offers both physical and mental health benefits. Taking magnesium supplements before or after practising yoga can help you with:
Reduced Anxiety
Emotional Balance
Increased Focus
Improved Body-Mind Connection
8. How does yoga and magnesium impact women's fitness and hormone balance?
Yoga can be an integral part of a woman’s fitness regimen. It can boost physical fitness and also help with endocrine health. Certain yoga poses can regulate hormonal balance. Magnesium, among its various health benefits, also regulates hormonal balance. Women, when practicing yoga or doing exercises, may need support for
Relief from muscle cramps
Muscle recovery
Energy production
Magnesium can be useful in alleviating muscular soreness and discomfort so that women can continue their yoga journey and improve their mind and body fitness.
References:
1) https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10745813/
2) https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Magnesium-Consumer/